Quick take: Natural rubber (NR) comes to market as latex concentrates, sheet/crepe rubbers, and technically specified rubber (TSR). TSR is sold under country brand systems like SMR (Malaysia), STR (Thailand), SIR (Indonesia), SVR (Vietnam), graded by lab metrics such as dirt, ash, nitrogen, volatile matter (VM), Wallace Plasticity (Po), Plasticity Retention Index (PRI), Mooney viscosity, and sometimes Lovibond color. Choose the type by process needs (e.g., dipping foams use latex), property targets, and supply risk.
The Short Answer & When “Type” Matters
“Type” refers to how NR is processed and graded before compounding. A tire factory might prefer TSR 20 blocks for bulk compounding, while a glove maker needs HA/LA latex concentrate with tight protein/ammonia control. Chemistry is still cis-1,4-polyisoprene, but impurity levels, plasticity, and viscosity differ by type and grade.
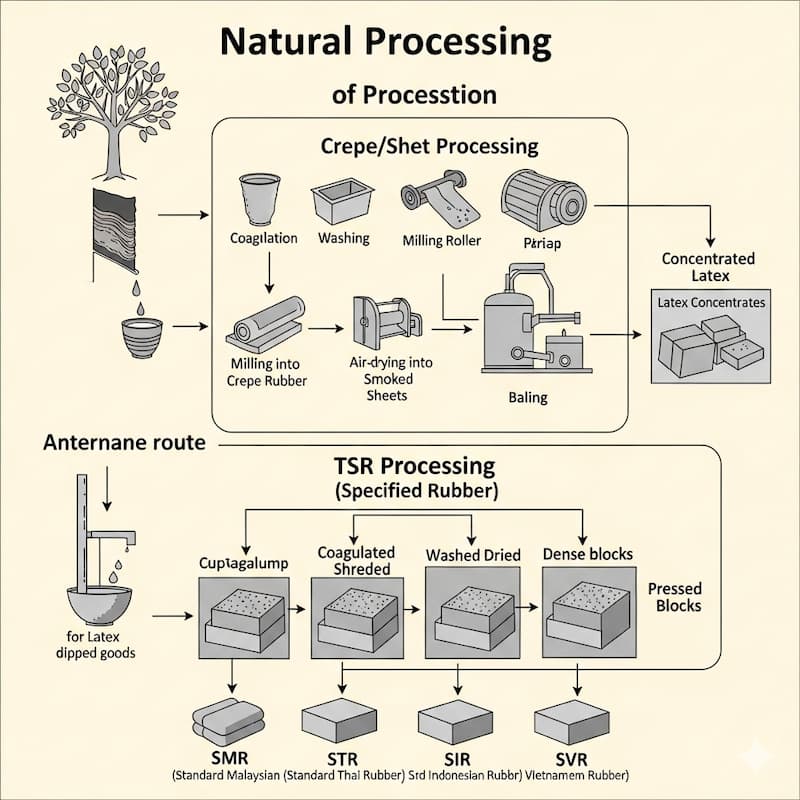
The Major Families of Natural Rubber
1) Latex concentrates (HA / LA / creamed)
- What it is: Field latex preserved with ammonia, then centrifuged or creamed to ~60% DRC (dry rubber content).
- Common subtypes: HA (High Ammonia), LA (Low Ammonia); creamed variants. Relevant specifications are covered by ISO latex standards (e.g., low-protein NR latex, types HA/LA).
- Used for: Dipped goods (gloves, balloons), adhesives, foam, thread.
- Why it matters: Protein/ammonia and mechanical stability affect dipping line yield and allergen risk in some uses.
2) Sheet rubbers: RSS (Ribbed Smoked Sheet) & ADS (Air-Dried Sheet)
- What it is: Coagulated latex rolled into ribbed sheets; RSS is visually graded (e.g., RSS1–RSS5) after smoking/drying; ADS uses hot-air drying.
- Used for: General goods and compounding where visual grading is acceptable; legacy routes remain common in parts of the supply chain.
3) Crepe rubbers: Pale crepe, Estate brown crepe, Skim crepe
- What it is: Sheets formed on creping rolls from high-purity latex (pale crepe) or reclaimed/skim streams (brown/skim).
- Used for: Specialty compounds where light color or cleanliness is important (e.g., medical goods, adhesives).
4) Technically Specified Rubber (TSR) — “Block rubber”
- What it is: Lab-graded bulk rubber, produced from field latex, cup lump/field coagulum, or blends; molded into blocks (bales).
- How it’s graded: By dirt, ash, nitrogen, volatile matter (VM) and performance indices like Po (Wallace plasticity) and PRI, plus sometimes Mooney viscosity and Lovibond color.
- Common grades: TSR 5 / 10 / 20, TSR CV (constant viscosity), TSR L (light color).
- Country brands: SMR (Malaysia), STR (Thailand), SIR (Indonesia), SVR (Vietnam); each aligns to comparable TSR classes with local specs.
Standards pointer: ISO provides guidance for TSR specification and grading, while latex concentrates have distinct ISO specifications (e.g., low-protein HA/LA). Ask suppliers for certificate of analysis listing dirt/ash/N/VM, Po, PRI, Mooney against the applicable spec.
How TSR/SMR Grades Are Measured (and Why You Care)
Key lab metrics (what they mean):
- Dirt (%wt) — non-rubber solids; lower is cleaner.
- Ash (%wt) — inorganic residue; high ash can signal contamination.
- Nitrogen (%wt) — proteinaceous matter; affects aging and odor.
- Volatile matter (%wt) — moisture/volatiles; influences processing.
- Po (Wallace plasticity) — initial plasticity; relates to molecular weight/gel content.
- PRI (Plasticity Retention Index) — resistance of plasticity to oxidative aging during mastication; higher = better retention.
- Mooney viscosity (ML 1+4 @100 °C) — processing viscosity window; CV grades hold a narrow band.

Table 1 — Representative SMR requirements (indicative; verify supplier COAs)
| Parameter | SMR L (latex) | SMR 10 | SMR 20 | SMR CV (50/60) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Dirt (max, %wt) | 0.02 | 0.08 | 0.16 | 0.02 |
| Ash (max, %wt) | 0.50 | 0.75 | 1.00 | 0.50 |
| Nitrogen (max, %wt) | 0.60 | 0.60 | 0.60 | 0.60 |
| Volatile matter (max, %wt) | 0.50–0.80 | 0.80 | 0.80 | 0.80 |
| Po (min) | ≥35 | ≥30 | ≥30 | n/a |
| PRI (min) | ≥60 | ≥50 | ≥40–50 | ≥60 |
| Mooney target | — | — | — | 50/60 ± band |
Caption: Values reflect published SMR spec sheets; exact thresholds vary by document and grade revision. Always confirm the current spec from your supplier.
Where Each Type Fits: Use-Case Matrix

Table 2 — Typical uses with pros/cons
| Type | Common uses | Pros | Watch-outs |
|---|---|---|---|
| Latex (HA/LA/creamed) | Gloves, balloons, foam, thread, adhesives | Process-ready liquid; excellent film formation | Protein/allergen concerns; requires preservative management. ITeh Standards |
| RSS / ADS | General goods, legacy compounding | Visual grades, traditional supply | Visual grading is less precise than TSR metrics. megavietnam.vn |
| Crepe (pale/brown/skim) | Light-colored goods, specialty | High cleanliness (pale crepe) | Limited availability; cost premium vs. general TSR. megavietnam.vn |
| TSR 5/10/20 | Tires, belts, bulk goods | Quantified cleanliness & stability; global supply | Grade choice affects processing & consistency. Harwick Standard |
| TSR CV / L | Precision compounding; color-sensitive | Constant viscosity; light color options | CV adds cost; ensure CV band matches your mill settings. barenagroup.com |
2024–2025 Supply & Sourcing Notes
Industry outlooks indicate a 2025 natural rubber shortfall (demand ~15.6 Mt vs. supply ~14.9 Mt), sustaining firm prices after late-2024 highs. Procurement teams should qualify alternates (e.g., SMR 10↔20 or CV↔non-CV where feasible), hold safety stock, and lock spec windows around Mooney/PRI to protect processing consistency.
FAQ
- What are the main types of natural rubber? Latex concentrates (HA/LA/creamed), sheet rubbers (RSS/ADS), crepe rubbers, and TSR block rubber (e.g., SMR/STR/SIR/SVR).
- What does TSR 5/10/20 mean? TSR classes reflect cleanliness and properties measured in the lab (e.g., dirt/ash/N/VM, Po/PRI). Lower numbers are higher-grade sources; 20 is a widely used field grade.
- What is SMR and how is it specified? Standard Malaysian Rubber—a country brand for TSR with published limits (e.g., dirt, ash, nitrogen, VM; Po/PRI; color).
- What’s the difference between HA and LA latex? HA has higher ammonia for preservation; LA uses less ammonia—specs appear in ISO latex documents (including low-protein variants).
- When should I buy CV (constant-viscosity) grades? When your process needs a tight Mooney window for mixing/viscosity control; CV keeps batches more consistent.
- Is RSS still relevant vs. TSR? RSS is visually graded; TSR provides quantified lab metrics, which many buyers prefer for consistency.
- Are 2025 supplies tight? Yes—industry groups forecast a production shortfall, supporting firm prices; plan alternates and stock. Reuters
- Does “type” change final properties? Type affects cleanliness/viscosity/oxidation stability entering compounding; final properties still depend on your compound and cure.


